Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
徐 平光; 山本 和喜; Harjo, S.; 菖蒲 敬久; 岩本 ちひろ*; 高村 正人*; 大竹 淑恵*; 小貫 祐介*; 佐藤 成男*; Liss, K.-D.*
no journal, ,
Texture as crystallographic preferred orientation of polycrystalline materials has attracted broad attention due to its important effects on mechanical and physical characteristics. Within both metals and ceramics, widespread applications of texture involve capabilities and simulations in sheet forming, additive manufacturing, while rocks and minerals also demonstrate such feature due to forming processes within the earth. Neutron diffraction can collect high statistical diffractograms due to an excellent penetration and a coarse beam spot, valuable for bulk investigations of microstructural changes and a characteristic response from polycrystalline materials. However, the available neutron instruments are quite limited in the world. We have developed various neutron texture measurement techniques using RESA at JRR-3, TAKUMI and iMATERIA at J-PARC, WOMBAT at ANSTO, and RANS at RIKEN, and obtained the following consensus: for a steady neutron source, the utilization of large area curved detectors together with multiple wavelengths texture analysis technique enables rapid and high precision angle dispersive neutron diffraction measurement; for a pulsed neutron source, the utilization of an optimized detector optical system with proper stereographic angle resolution ( 2
2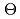


 ) and instrumental resolution (
) and instrumental resolution ( d/d) is much more valuable for improving the reliability of the time-of-flight neutron diffraction measurement, enabling the orientation feature of tiny amounts of a second phase in a round robin textured limestone sample has been recognized satisfactorily. For a compact neutron source, the selective usage of a high signal-to-noise ratio as well as the wavelength ranges of the time-of-flight neutron diffraction patterns obtained from an in-house texture measurement are effective to reduce the diffraction uncertainty during Rietveld texture analysis, improving instrumental accessibility for on-site applications.
d/d) is much more valuable for improving the reliability of the time-of-flight neutron diffraction measurement, enabling the orientation feature of tiny amounts of a second phase in a round robin textured limestone sample has been recognized satisfactorily. For a compact neutron source, the selective usage of a high signal-to-noise ratio as well as the wavelength ranges of the time-of-flight neutron diffraction patterns obtained from an in-house texture measurement are effective to reduce the diffraction uncertainty during Rietveld texture analysis, improving instrumental accessibility for on-site applications.
Zhang, Y.*; 梅田 岳昌*; 宮本 吾郎*; 古原 忠*; 諸岡 聡
no journal, ,
Essential understanding of the pearlite growth kinetics is important to predict the lamellar spacing and the resultant mechanical properties of pearlitic steels. In this study, through quantitatively analyzing the microstructural features in the vicinity of pearlite growth interface, the influence of these factors and the underlying thermodynamics of pearlite growth kinetics were clarified. The pearlite growth rate and lamellar spacing were measured based on the microstructural observation via optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, respectively. Three-dimensional atom probe (3DAP) was used to analyze the elemental distribution in the vicinity of pearlite growth front, whereas in-situ neutron diffraction at elevated temperatures was performed at J-PARC, BL19 (TAKUMI) to quantify the elastic strain generated during pearlite transformation. Based on the proposed thermodynamic model, the influence of various factors on the pearlite growth kinetics is estimated using the experimental results obtained in this study. It was found that in most transformation conditions, solute drag effects caused by Mn interfacial segregation have the largest contribution in retarding the pearlite growth rate. In contrast, the magnitude of elastic strain in pearlite measured by neutron diffraction is quite small, which marginally affects the pearlite growth kinetics.
丸澤 賢人*; Zhang, Y.*; 宮本 吾郎*; 古原 忠*; 諸岡 聡
no journal, ,
マルテンサイトの焼もどし過程は反応熱と熱膨張の物性測定結果よると、合金元素添加により反応が遅延される傾向があると報告されているが、ミクロ組織変化との対応には不明な点が多く残されている。本研究では種々の組織解析手法を組み合わせることで、低温焼もどし時の組織変化に及ぼす合金元素添加の影響を解明することを目的とした。測定試料に対して、室温から600 Cまで10
Cまで10 C/minの連続加熱中および90
C/minの連続加熱中および90 Cでの等温保持中のその場中性子回折測定を行った。また種々の温度と時間で焼もどし後のX線回折測定およびミクロ組織観察を行った。中性子回折の結果から、焼入れままの状態では残留オーステナイトのピークが確認され、また強制固溶された炭素により正方晶性(軸比)を有するためマルテンサイトの002回折ピークには明瞭なピーク分離が生じている。一方で、昇温に伴って第2段階の終了温度である300
Cでの等温保持中のその場中性子回折測定を行った。また種々の温度と時間で焼もどし後のX線回折測定およびミクロ組織観察を行った。中性子回折の結果から、焼入れままの状態では残留オーステナイトのピークが確認され、また強制固溶された炭素により正方晶性(軸比)を有するためマルテンサイトの002回折ピークには明瞭なピーク分離が生じている。一方で、昇温に伴って第2段階の終了温度である300 C付近で残留オーステナイトのピークは消失し、またピーク分離は徐々に解消され正方晶性が低下した。この傾向は他の合金材についても同様であった。次に、軸比の変化に着目すると、焼入れままではAl添加材はその他の合金材と比べ、最も高い軸比を有しており、その後遅延効果により第1段階後期まで正方晶性が維持され、200
C付近で残留オーステナイトのピークは消失し、またピーク分離は徐々に解消され正方晶性が低下した。この傾向は他の合金材についても同様であった。次に、軸比の変化に着目すると、焼入れままではAl添加材はその他の合金材と比べ、最も高い軸比を有しており、その後遅延効果により第1段階後期まで正方晶性が維持され、200 CでFe-C2元合金と一致した。一方でFe-C2元合金と比べ、Mn, Cr添加材の軸比変化はほとんど同様で、Si添加材は第0段階で軸比低下がわずかに促進されるという結果が得られた。
CでFe-C2元合金と一致した。一方でFe-C2元合金と比べ、Mn, Cr添加材の軸比変化はほとんど同様で、Si添加材は第0段階で軸比低下がわずかに促進されるという結果が得られた。
五十嵐 誉廣; 大谷 恭平; 青山 高士
no journal, ,
橋梁やプラント等の大型構造物の健全性評価は重要課題の一つである。大型構造物の主要材料の一つである鉄鋼材料の腐食メカニズムを理解し材料健全性評価に応用するため、暴露試験や実験室における乾湿繰り返し試験等、多くの研究がなされている。また外観写真から腐食状態を予測する研究もなされており、破壊検査を行うことができない現物の腐食量を予測する手法として有用な方法の一つと考えられる。本報では、乾湿繰り返し試験を行った炭素鋼試験片の錆落とし前の外観写真に対してFAST特徴点抽出法を適用することにより、腐食深さの絶対値の予測は難しいが腐食位置については凡そ予測できることを示した。